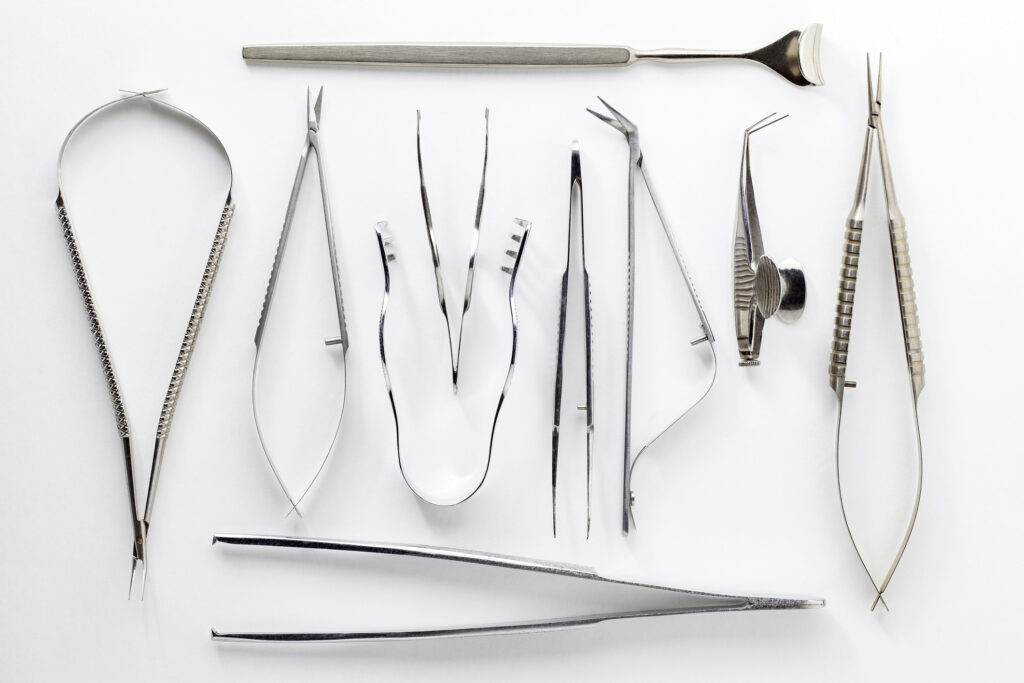
Medical devices and components have become an essential part of modern healthcare. These devices play a crucial role in diagnosing, treating, and monitoring patients. However, to ensure the safety and effectiveness of these devices, they require high-quality finishing and coating services. Finishing and coating services provide several benefits, including improved functionality, durability, and safety.
Metal coatings and metal finishing processes are both used in the medical industry to enhance the properties of medical devices and components, but they differ in their applications and processes.
Metal finishing processes, such as deburring, passivation, polishing, and ultrasonic cleaning, are used to improve the surface finish and remove any unwanted burrs, sharp edges, or surface imperfections from the metal components. These processes help to improve the aesthetic appearance of the part, reduce the risk of contamination, and enhance the functionality and durability of the component.
On the other hand, metal coatings are applied to the surface of the medical device or component to provide additional properties, such as biocompatibility, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, or electrical conductivity. These coatings are applied through a variety of methods, including electroplating, physical vapor deposition, and chemical vapor deposition.
The main difference between metal coatings and metal finishing processes is that coatings are a layer of material that is applied to the surface of the component, while finishing processes alter the surface of the component itself. Metal coatings can also provide additional properties to the surface of the component, whereas finishing processes primarily enhance the surface finish and remove surface imperfections.
Another key difference is that metal coatings require a more complex and precise process than metal finishing processes. Metal coatings require specific environmental conditions, such as temperature and pressure, and precise control over the deposition process to ensure that the coating adheres to the substrate and provides the desired properties.
Types of Finishes Used for Medical Devices and Components
Here are several types of finishes that are used in the manufacturing of medical instruments and equipment components:
Deburring – Deburring is the process of removing burrs, sharp edges, and other unwanted material from the surface of a part. The process involves using abrasive tools to remove the burrs and edges manually or through an automated process. This process ensures that the surface of the part is smooth, free from sharp edges, and safe to handle. The results from deburring include improved safety by removing sharp edges, reducing the risk of contamination by removing surface imperfections and improved aesthetics. Products and components that can benefit from deburring include surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and catheter components.
Passivation – Passivation is a chemical process used to remove free iron and other contaminants from the surface of a part. The process involves immersing the part in a nitric acid bath to remove the contaminants and create a passive layer on the surface of the part. This layer provides resistance to corrosion and enhances the biocompatibility of the part, and therefore reduces the risk of contamination. Passivation is frequently used in the finishing process of medical implants, surgical instruments, and dental implants.
Polishing – Polishing is a process that involves using abrasive tools and compounds to create a smooth and shiny surface on a part. The process can be manual or automated, and it removes surface imperfections, scratches, and stains. Polishing improves the aesthetics of the part, making it more attractive and easier to clean and reducing the risk of contamination. A polished finish is often used for surgical instruments, dental instruments and endoscopes.
Ultrasonic Cleaning – Ultrasonic cleaning is a process that uses high-frequency sound waves to remove contaminants from the surface of a part. The process involves immersing the part in a cleaning solution and using an ultrasonic cleaner to create sound waves that agitate the solution, removing contaminants from the surface of the part. It is highly effective at removing contaminants from complex shapes and sizes without being destructive to the part. Ultrasonic is used for items such as surgical instruments, endoscopes and catheters.
Types of Finishes Used for Medical Devices and Components
Metal coatings are commonly used in medical devices and components to enhance their properties, such as biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance. Some of the metal coatings we offer at AMF Technologies include anodizing, sulfamate nickel, bright nickel, electroless nickel, black oxide, and zinc.
Anodizing – Anodizing involves the process of creating an oxide layer on the surface of the device. This process provides several benefits, such as improved corrosion resistance, improved biocompatibility, and improved wear resistance. Anodizing is commonly used in the production of orthopedic implants, dental implants, and surgical instruments.
Sulfamate Nickel – Sulfamate Nickel is a type of electroplating process that deposits a layer of nickel onto a metal substrate. This coating is commonly used for medical devices and components due to its excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Sulfamate Nickel is also used for wear resistance and as an undercoating for other types of metal coatings. Medical parts that benefit from Sulfamate Nickel coating include surgical instruments, implants, and other medical devices that require a durable and corrosion-resistant finish.
Bright Nickel – Bright Nickel is a type of electroplating process that deposits a layer of bright, shiny nickel onto a metal substrate. This coating provides excellent corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and an attractive finish. Bright Nickel is commonly used for medical devices and components that require a high-quality, decorative finish, such as orthodontic braces, dental implants, and other medical devices that are visible to the patient.
Electroless Nickel – Electroless Nickel is a type of plating process that deposits a layer of nickel onto a metal substrate without the use of an electric current. This coating provides excellent corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and uniform thickness. Electroless Nickel is commonly used for medical devices and components that require a durable and corrosion-resistant finish, such as surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and other medical devices that are exposed to harsh environments.
Black Oxide – Black Oxide is a type of chemical conversion coating that creates a black finish on a metal substrate. This coating provides excellent corrosion resistance and an attractive, non-reflective finish. Black Oxide is commonly used for medical devices and components that require a non-reflective finish, such as scopes, endoscopic instruments, and other medical devices used in low-light environments.
Zinc – Zinc is a type of plating process that deposits a layer of zinc onto a metal substrate. This coating provides excellent corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and is RoHS compliant. Zinc plating is commonly used for medical devices and components that require a durable and corrosion-resistant finish, such as surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and other medical devices that are exposed to harsh environments.
Metal coatings and metal finishing processes are both essential in the production of high-quality medical devices and components. While finishing processes primarily alter the surface of the component, coatings provide additional properties to the surface. Both processes require precision and careful control to ensure that the final product meets the required standards and specifications.
Got any surface coating or finishing questions? We’ve got answers! Contact us today!